Comprehensive Analysis of Mental Health Trends in California, 2025
California's mental health landscape continues to evolve in 2025, marked by rising demand for services, widening disparities, and new challenges arising from environmental and social factors. This analysis presents an in-depth, data-driven overview based on sources such as the California Health Care Foundation, Mental Health America, and state health authorities.
1. Accessibility Challenges in Mental Health Care
Low-income Californians face the most significant barriers, with cost and provider shortages leading to delayed or foregone care. Nearly 74% of low-income individuals cite expense as a major barrier, reinforcing systemic inequities in access (CHCF 2024 Health Policy Survey).
2. Youth Mental Health: Increasing Concerns
*2025 figures are preliminary estimates based on trends. The youth mental health crisis is worsening, with nearly 1 in 3 adolescents affected by depression or anxiety, and significant treatment gaps remain (Mental Health America 2024 Report).
3. Demographic Disparities in Mental Health Outcomes
These disparities emphasize that Black and Latino males experience high psychological distress but have markedly lower treatment rates compared to White counterparts, raising equity concerns (CHCF Behavioral Health Data Landscape 2024).
4. Mental Health in the Criminal Justice System
High incarceration rates among individuals with mental health issues highlight the critical need for improved mental health services both inside institutions and in community diversion alternatives (CHCF 2024 Behavioral Health Report).
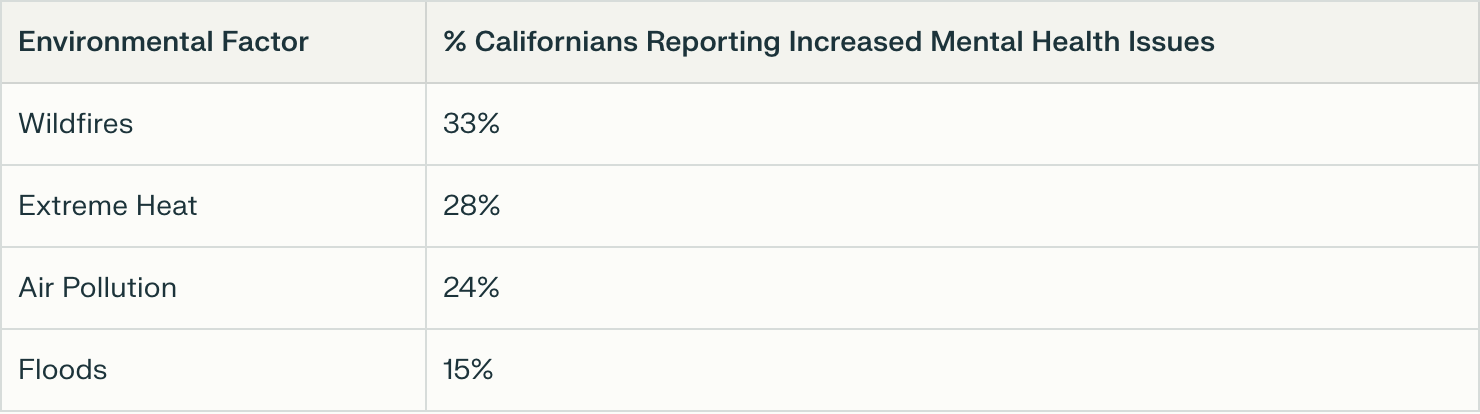
5. Mental Health and Environmental Stressors
Increasing environmental stressors from climate change contribute to heightened mental health strain, indicating the need for specialized trauma-informed mental health programs (CHCF Health Policy Poll 2024).
6. Comparing California with National Averages
While California’s suicide rate remains lower than the national average, the state experiences a higher prevalence of mental illness and a larger treatment gap, underscoring persistent access issues (Mental Health America 2024).
Conclusion
California’s mental health challenges in 2025 require urgent attention through equitable funding, expanded access to culturally competent care, youth-targeted services, and integration of environmental mental health considerations. Implementing systemic reforms in service delivery and social support will be essential to meeting the growing and diverse needs of Californians.
Sources:
https://roblesranch.com/california-mental-health-statistics-2025/
https://www.dhcs.ca.gov/provgovpart/Documents/Draft-2025-SNAP-Report.pdf
https://www.chcf.org/resource/mental-health-california-almanac/
https://hcai.ca.gov/data/data-and-reports/behavioral-health/
https://calmatters.org/health/mental-health/2025/06/prop-1-mental-health-awards/
https://www.nami.org/about-mental-illness/mental-health-by-the-numbers/